Deep Vein Thrombosis Explained: How to Identify and Prevent This Serious Condition
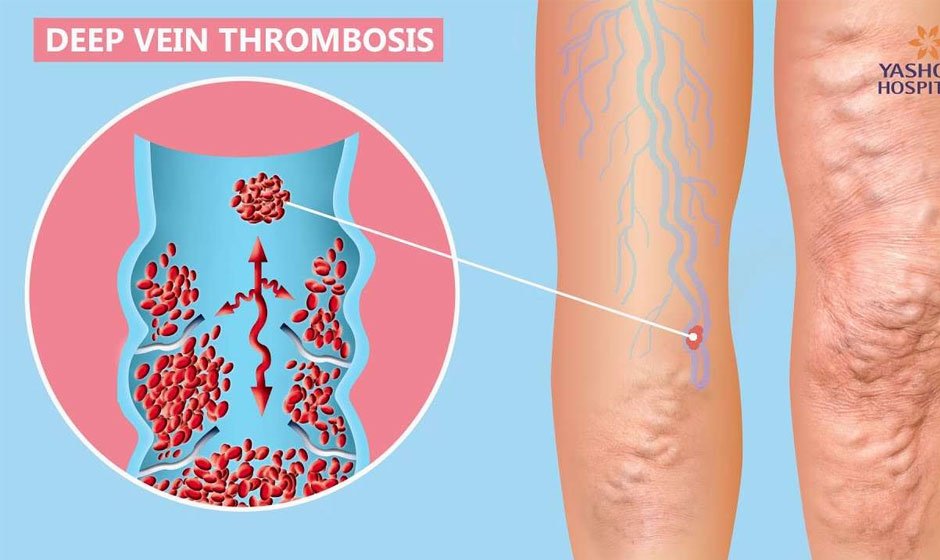
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a severe medical condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, typically in the legs. Understanding and recognizing the early signs of DVT is crucial for timely treatment and prevention of complications such as pulmonary embolism.
This article delves into the symptoms of DVT, the importance of early detection, and practical strategies for preventing deep vein thrombosis. Being informed and proactive can make a significant difference in managing this condition.
Symptoms of Deep Vein Thrombosis
Swelling in One Leg
One of the most common symptoms of DVT is swelling in one leg. The affected leg may become noticeably more prominent than the other. This swelling occurs because the blood clot obstructs normal blood flow, causing fluid to build up in the tissues.
Pain or Tenderness
Pain or tenderness in the leg, particularly when standing or walking, is another crucial sign. This pain often starts in the calf and can feel like cramping or soreness. If the pain is accompanied by swelling, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly.
Red or Discolored Skin
The skin over the affected area may become red or have a bluish tinge. This discoloration occurs due to the disruption of blood flow and the buildup of blood behind the clot. The skin might also feel warm to the touch.
Visible Veins
In some cases, veins near the surface of the skin become more visible or prominent. This happens as blood finds alternative pathways around the clot, causing the superficial veins to swell and become noticeable.
Warmth in the Affected Leg
Warmth in the area of the clot is another symptom to watch for. This warmth results from inflammation caused by the blood clot. When combined with swelling and pain, it can be a strong indicator.
The Importance of Early Detection
Preventing Complications
Early detection is vital to prevent serious complications. If left untreated, a blood clot can break loose and travel to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism. This condition can be life-threatening, leading to severe respiratory issues or even death.
Avoiding Long-Term Damage
Timely treatment can also prevent long-term damage to the veins. Chronic venous insufficiency, where the veins cannot pump enough blood back to the heart, can develop if it is not treated properly. This can result in persistent pain, swelling, and skin changes in the affected leg.
Improving Treatment Outcomes
The earlier it is detected, the more effective the treatment will be. Medications such as anticoagulants can help dissolve the clot and prevent new ones from forming. In some cases, medical procedures may be necessary to remove the clot.
Preventing Deep Vein Thrombosis
Stay Active
Regular physical activity is one of the most effective ways of preventing deep vein thrombosis. Exercise helps improve blood circulation and prevents the formation of clots. Even simple activities like walking or stretching can make a significant difference, especially for individuals who sit or stand for long periods.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Being overweight increases the risk of DVT, as excess weight puts additional pressure on the veins in the legs. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can reduce this risk and improve overall vascular health.
Stay Hydrated
Dehydration can cause blood to thicken, making it more prone to clotting. Drinking plenty of fluids, particularly water, helps keep the blood thin and reduces the risk of clot formation.
Avoid Prolonged Immobility
Long periods of immobility, such as during long flights or car rides, can increase the risk of DVT. Taking breaks to move around and stretch the legs is crucial. When traveling, consider wearing compression stockings to improve blood flow in the legs.
Wear Compression Stockings
Compression stockings apply gentle pressure to the legs, promoting blood flow and reducing the risk of clots. They are particularly beneficial for individuals at higher risk of DVT, such as those with a history of the condition or those who are immobile for extended periods.
Monitor Medications
Certain medications, including birth control pills and hormone replacement therapy, can increase the risk of DVT. It is essential to discuss any concerns with a healthcare provider and explore alternative options if necessary.
Stay Informed
Awareness and education are vital in preventing DVT. Understanding the risk factors, symptoms, and prevention strategies can empower individuals to take proactive steps to reduce their risk. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can also help monitor vascular health and identify any potential issues early.
Recognizing the early signs of Deep Vein Thrombosis and understanding the importance of early detection can significantly impact outcomes. By being aware of the symptoms, individuals can seek timely medical attention. Staying informed and proactive is the best approach to managing and preventing this severe condition.