The Rise of Flex PCBs: Flexible Solutions for Modern Electronics
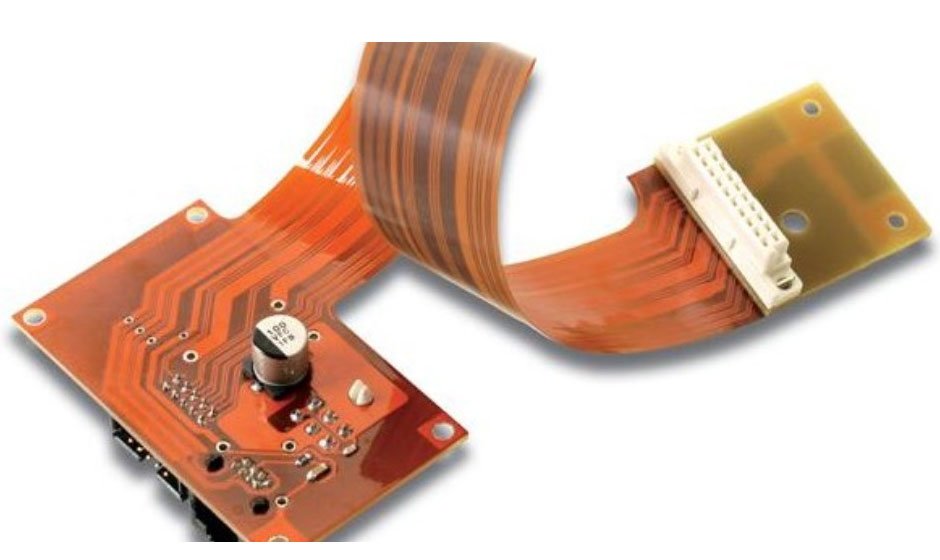
The electronics sector continues to advance at an astounding rate in today’s fast-paced world. With consumers demanding smaller, more versatile, and high-performance electronic devices, manufacturers have had to adapt. One of the most significant innovations in recent years is the widespread adoption of Flex PCBs (Flexible Printed Circuit Boards). These remarkable flexible solutions have transformed the landscape of modern electronics, offering numerous advantages that cater to a wide range of applications, including ELE PCB Manufacturing, ELE PCB Assembly, and much more.
The Birth of Flex PCBs
Flex PCBs, also known as flex circuits or flexible electronics, represent a departure from the traditional rigid PCBs that have been the industry standard for decades. The demand for electronics that are not only compact but also adaptable to various form factors necessitated the exploration of alternative solutions. As a result, Flex PCBs were created as a reaction to these changing needs.
The concept of flexible circuits dates back to the mid-20th century, with early applications primarily focused on the military and aerospace sectors. Flex PCB potential increased along with technological development. Today, these circuits are an integral part of a wide array of everyday devices, from smartphones and wearables to automotive systems and even medical implants.
Why Flex PCBs Are on the Rise
- Space-Efficiency
One of the main factors contributing to Flex PCBs’ rising popularity is their exceptional space efficiency. Traditional rigid PCBs, by nature, are bulky and inflexible, which limits their use in innovative designs. Contrarily, flex PCBs can be folded, twisted, and bent to fit into small, awkward locations. Because of this characteristic, they are the ideal choice for products where space is at a premium.
- Weight Reduction
In applications such as aerospace and automotive, weight is a critical factor. Flex PCBs are significantly lighter than rigid PCBs, contributing to an overall reduction in weight. This weight savings enhances fuel efficiency and enables the development of sleeker and more aerodynamic designs.
- Durability and Reliability
Flex PCBs are recognized for their longevity and reliability. They can tolerate repeated bending, flexing, and dynamic movements without losing their functionality. This makes them ideal for products subjected to constant motion or mechanical stress. Additionally, their performance remains consistent even in challenging conditions due to their resilience to shock and vibration.
- Design Freedom
The flexibility of these circuits opens up a world of design possibilities. Engineers and designers can experiment with form factors previously unattainable with rigid PCBs. This newfound design freedom allows for creative and innovative solutions, resulting in more ergonomic and aesthetically pleasing products.
- Cost-Efficiency
While the initial manufacturing cost of Flex PCBs may be slightly higher than that of rigid PCBs, the overall cost savings become evident over the product’s lifecycle. Their robustness and dependability lessen the need for frequent replacements, which saves money over the long haul. Additionally, their compact size can lead to material and assembly savings.
- Enhanced Performance
In some cases, Flex PCBs can offer superior electrical performance. Signal integrity may be improved, and electromagnetic interference (EMI) may be reduced due to the shorter connector lengths and less parasitic capacitance and inductance. This enhanced performance is particularly valuable in high-frequency and high-speed applications.
Applications of Flex PCBs
Flex PCBs are used in a variety of goods and sectors, including but not limited to:
- Consumer Electronics
The consumer electronics industry has warmly embraced Flex PCBs in smartphones, tablets, and wearables. The flexibility of these circuits allows for thinner and lighter designs, while their durability ensures a longer product lifespan.
- Aerospace and Aviation
In aerospace and aviation, where weight reduction and space optimization are paramount, Flex PCBs are used in avionics, satellites, and communication systems. They contribute to reduced fuel consumption and enhanced communication capabilities.
- Medical Devices
Flex PCBs play a vital role in the medical field, where they are used in devices like pacemakers, defibrillators, and medical imaging equipment. Their flexibility allows for implantable devices that conform to the body’s contours, improving patient comfort and safety.
- Automotive
The automotive industry uses flex PCBs in several applications, including ADAS, infotainment, and airbag systems. Their lightweight and durable nature enhances vehicle performance and safety.
- Industrial Automation
In industrial settings, where machinery and equipment undergo constant movement and vibration, Flex PCBs are used in control systems and sensors, ensuring reliable operation and minimizing downtime.
- Military and Defense
Flex PCBs have long been a staple in military and defense applications, where ruggedness and reliability are paramount. They are utilized in military vehicles, radar equipment, and communication systems. Specific PCB variations.
Specialized PCB Variants
In addition to Flex PCBs, there are several specialized PCB variants that cater to specific needs:
- HDI PCB (High-Density Interconnect PCB)
High component density and fine-line trace patterns are hallmarks of HDI PCBs. They are often used in applications requiring miniaturization and increased functionality, such as smartphones and high-performance computing.
- MCPCB (Metal Cored PCB)
MCPCBs have a metal core, typically aluminum or copper, that provides excellent heat dissipation. These PCBs are essential in applications where thermal management is critical, such as LED lighting and power electronics.
- Rigid Flex PCB
Flex PCBs’ flexibility is combined with the rigidity of conventional PCBs in stiff Flex PCBs. They are used in applications requiring flexibility and structural support, such as in foldable smartphones and aerospace systems.
- Multilayer PCB
Copper traces and insulating material are arranged in layers on multilayer PCBs. They are used in complex electronic devices where numerous interconnections are necessary, such as computer motherboards and network switches.
What is HDI PCB?
The printed circuit board, an HDI PCB or High-Density Interconnect PCB, is a unique variety that provides high component density and precision. These boards are characterized by their intricate and compact trace patterns, enabling the placement of many components in a small area. HDI PCBs are designed to accommodate the miniaturization trend seen in modern electronics, making them a perfect fit for applications like smartphones, tablets, and high-performance computing.
The Future of Flex PCBs
The potential for Flex PCBs in the future is exciting as technology develops. Innovations in materials and manufacturing techniques are likely to produce even thinner and more flexible PCBs. Additionally, the integration of flexible displays and organic electronics is set to revolutionize the field further. Flex PCBs’ adaptability and versatility position them at the forefront of these developments.
In conclusion, the rise of Flex PCBs marks a significant shift in the world of electronics. Their unique combination of space efficiency, weight reduction, durability, design freedom, cost-efficiency, and enhanced performance has made them indispensable in various industries. From consumer electronics to aerospace, medical devices, and beyond, Flex PCBs are driving today’s innovations and shaping the technologies of tomorrow. As the boundaries of electronics continue to expand, Flex PCBs are set to play a pivotal role in our technological evolution along.